Sending and Receiving data using send and recv commands with MPI
comm.recv() and comm.send()
Since the main idea of MPI is to send and receive messages, I think it'd be a good idea to go ahead and cover that.
There are many ways to send and receive data, we'll cover the most direct method first, in its most basic form. There are many ways to send and receive data, however:
- one to one - one node to another.
- one to many - one node to all nodes or many of them.
- many to one - many nodes, or all nodes, to one node (usually the master).
from mpi4py import MPI
import time
comm = MPI.COMM_WORLD
rank = comm.rank
size = comm.size
name = MPI.Get_processor_name()
shared = (rank+1)*5
if rank == 0:
data = shared
comm.send(data, dest=1)
comm.send(data, dest=2)
print 'From rank',name,'we sent',data
time.sleep(5)
elif rank == 1:
data = comm.recv(source=0)
print 'on node',name, 'we received:',data
elif rank == 2:
data = comm.recv(source=0)
print 'on node',name, 'we received:',data
Sending and receiving data in the basic form is pretty simple using comm.send and comm.recv (short for receive).
We're using two parameters in comm.send. The first parameter is the data that we want to send, which we're calling data. The next parameter is the destination, or the node number.
To receive, we're just using one parameter, which is source, or what node are we expecting this data to come from.
After that, we're printing to console any data that we have.
mpirun.openmpi -np 3 -machinefile /home/pi/mpi_testing/machinefile python ~/Desktop/sct/sct5.py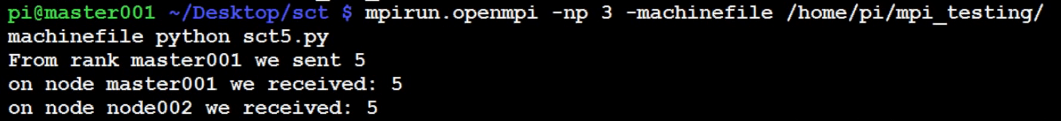
-
Build a Supercomputer with Raspberry Pis
-
Intro
-
Supplies
-
Installing Operating System
-
Downloading and installing MPI
-
Testing Supercomputer
-
MPI with MPI4py Introduction
-
Installing mpi4py for use with Python and MPI
-
First basic MPI script with mpi4py
-
Using conditional, Python, statements alongside MPI commands example
-
Getting network processor size with the size command
-
Sending and Receiving data using send and recv commands with MPI
-
Dynamically sending messages to and from processors with MPI and mpi4py
-
Message and data tagging for send and recv MPI commands tutorial
-
MPI broadcasting tutorial with Python, mpi4py, and bcast
-
Scatter with MPI tutorial with mpi4py
-
Gather command with MPI, mpi4py, and Python