Reinforcement Learning in Action - Self-driving cars with Carla and Python part 5
Welcome to part 5 of the self-driving cars and reinforcement learning with Carla, Python, and TensorFlow.
Now that we've got our environment and agent, we just need to add a bit more logic to tie these together, which is what we'll be doing next.
Full code up to this point:
import glob
import os
import sys
import random
import time
import numpy as np
import cv2
import math
from collections import deque
from keras.applications.xception import Xception
from keras.layers import Dense, GlobalAveragePooling2D
from keras.optimizers import Adam
from keras.models import Model
try:
sys.path.append(glob.glob('../carla/dist/carla-*%d.%d-%s.egg' % (
sys.version_info.major,
sys.version_info.minor,
'win-amd64' if os.name == 'nt' else 'linux-x86_64'))[0])
except IndexError:
pass
import carla
SHOW_PREVIEW = False
IM_WIDTH = 640
IM_HEIGHT = 480
SECONDS_PER_EPISODE = 10
REPLAY_MEMORY_SIZE = 5_000
MIN_REPLAY_MEMORY_SIZE = 1_000
MINIBATCH_SIZE = 16
PREDICTION_BATCH_SIZE = 1
TRAINING_BATCH_SIZE = MINIBATCH_SIZE // 4
UPDATE_TARGET_EVERY = 5
MODEL_NAME = "Xception"
MEMORY_FRACTION = 0.8
MIN_REWARD = -200
EPISODES = 100
DISCOUNT = 0.99
epsilon = 1
EPSILON_DECAY = 0.95 ## 0.9975 99975
MIN_EPSILON = 0.001
AGGREGATE_STATS_EVERY = 10
class CarEnv:
SHOW_CAM = SHOW_PREVIEW
STEER_AMT = 1.0
im_width = IM_WIDTH
im_height = IM_HEIGHT
front_camera = None
def __init__(self):
self.client = carla.Client("localhost", 2000)
self.client.set_timeout(2.0)
self.world = self.client.get_world()
self.blueprint_library = self.world.get_blueprint_library()
self.model_3 = self.blueprint_library.filter("model3")[0]
def reset(self):
self.collision_hist = []
self.actor_list = []
self.transform = random.choice(self.world.get_map().get_spawn_points())
self.vehicle = self.world.spawn_actor(self.model_3, self.transform)
self.actor_list.append(self.vehicle)
self.rgb_cam = self.blueprint_library.find('sensor.camera.rgb')
self.rgb.set_attribute("image_size_x", f"{self.im_width}")
self.rgb.set_attribute("image_size_y", f"{self.im_height}")
self.rgb.set_attribute("fov", f"110")
transform = carla.Transform(carla.Location(x=2.5, z=0.7))
self.sensor = self.world.spawn_actor(self.rgb_cam, transform, attach_to=self.vehicle)
self.actor_list.append(self.sensor)
self.sensor.listen(lambda data: self.process_img(data))
self.vehicle.apply_control(carla.VehicleControl(throttle=0.0, brake=0.0))
time.sleep(4)
colsensor = self.blueprint_library.find("sensor.other.collision")
self.colsensor = self.world.spawn_actor(colsensor, transform, attach_to=self.vehicle)
self.actor_list.append(self.colsensor)
self.colsensor.listen(lambda event: self.collision_data(event))
while self.front_camera is None:
time.sleep(0.01)
self.episode_start = time.time()
self.vehicle.apply_control(carla.VehicleControl(throttle=0.0, brake=0.0))
return self.front_camera
def collision_data(self, event):
self.collision_hist.append(event)
def process_img(self, image):
i = np.array(image.raw_data)
#print(i.shape)
i2 = i.reshape((self.im_height, self.im_width, 4))
i3 = i2[:, :, :3]
if self.SHOW_CAM:
cv2.imshow("", i3)
cv2.waitKey(1)
self.front_camera = i3
def step(self, action):
if action == 0:
self.vehicle.apply_control(carla.VehicleControl(throttle=1.0, steer=-1*self.STEER_AMT))
elif action == 1:
self.vehicle.apply_control(carla.VehicleControl(throttle=1.0, steer= 0))
elif action == 2:
self.vehicle.apply_control(carla.VehicleControl(throttle=1.0, steer=1*self.STEER_AMT))
v = self.vehicle.get_velocity()
kmh = int(3.6 * math.sqrt(v.x**2 + v.y**2 + v.z**2))
if len(self.collision_hist) != 0:
done = True
reward = -200
elif kmh < 50:
done = False
reward = -1
else:
done = False
reward = 1
if self.episode_start + SECONDS_PER_EPISODE < time.time():
done = True
return self.front_camera, reward, done, None
class DQNAgent:
def __init__(self):
self.model = self.create_model()
self.target_model = self.create_model()
self.target_model.set_weights(self.model.get_weights())
self.replay_memory = deque(maxlen=REPLAY_MEMORY_SIZE)
self.tensorboard = ModifiedTensorBoard(log_dir=f"logs/{MODEL_NAME}-{int(time.time())}")
self.target_update_counter = 0
self.graph = tf.get_default_graph()
self.terminate = False
self.last_logged_episode = 0
self.training_initialized = False
def create_model(self):
base_model = Xception(weights=None, include_top=False, input_shape=(IM_HEIGHT, IM_WIDTH,3))
x = base_model.output
x = GlobalAveragePooling2D()(x)
predictions = Dense(3, activation="linear")(x)
model = Model(inputs=base_model.input, outputs=predictions)
model.compile(loss="mse", optimizer=Adam(lr=0.001), metrics=["accuracy"])
return model
def update_replay_memory(self, transition):
# transition = (current_state, action, reward, new_state, done)
self.replay_memory.append(transition)
def train(self):
if len(self.replay_memory) < MIN_REPLAY_MEMORY_SIZE:
return
minibatch = random.sample(self.replay_memory, MINIBATCH_SIZE)
current_states = np.array([transition[0] for transition in minibatch])/255
with self.graph.as_default():
current_qs_list = self.model.predict(current_states, PREDICTION_BATCH_SIZE)
new_current_states = np.array([transition[3] for transition in minibatch])/255
with self.graph.as_default():
future_qs_list = self.target_model.predict(new_current_states, PREDICTION_BATCH_SIZE)
X = []
y = []
for index, (current_state, action, reward, new_state, done) in enumerate(minibatch):
if not done:
max_future_q = np.max(future_qs_list[index])
new_q = reward + DISCOUNT * max_future_q
else:
new_q = reward
current_qs = current_qs_list[index]
current_qs[action] = new_q
X.append(current_state)
y.append(current_qs)
log_this_step = False
if self.tensorboard.step > self.last_logged_episode:
log_this_step = True
self.last_log_episode = self.tensorboard.step
with self.graph.as_default():
self.model.fit(np.array(X)/255, np.array(y), batch_size=TRAINING_BATCH_SIZE, verbose=0, shuffle=False, callbacks=[self.tensorboard] if log_this_step else None)
if log_this_step:
self.target_update_counter += 1
if self.target_update_counter > UPDATE_TARGET_EVERY:
self.target_model.set_weights(self.model.get_weights())
self.target_update_counter = 0
def get_qs(self, state):
return self.model.predict(np.array(state).reshape(-1 *state.shape)/255)[0]
def train_in_loop(self):
X = np.random.uniform(size=(1, IM_HEIGHT, IM_WIDTH, 3)).astype(np.float32)
y = np.random.uniform(size=(1, 3)).astype(np.float32)
with self.graph.as_default():
self.model.fit(X,y, verbose=False, batch_size=1)
self.training_initialized = True
while True:
if self.terminate:
return
self.train()
time.sleep(0.01)
To start, we're going to just copy and paste the modified tensorboard class from the reinforcement learning tutorials:
from keras.callbacks import TensorBoard
...
# Own Tensorboard class
class ModifiedTensorBoard(TensorBoard):
# Overriding init to set initial step and writer (we want one log file for all .fit() calls)
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.step = 1
self.writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(self.log_dir)
# Overriding this method to stop creating default log writer
def set_model(self, model):
pass
# Overrided, saves logs with our step number
# (otherwise every .fit() will start writing from 0th step)
def on_epoch_end(self, epoch, logs=None):
self.update_stats(**logs)
# Overrided
# We train for one batch only, no need to save anything at epoch end
def on_batch_end(self, batch, logs=None):
pass
# Overrided, so won't close writer
def on_train_end(self, _):
pass
# Custom method for saving own metrics
# Creates writer, writes custom metrics and closes writer
def update_stats(self, **stats):
self._write_logs(stats, self.step)
As a reminder, the above code is meant to just simplify the amount of logging that TensorFlow/TensorBoard does. Normally, there's a log file per fitment, and a datapoint per step, which becomes very absurd, very quickly, with reinforcment learning (where you fit every step!).
Let's add the following imports:
import tensorflow as tf import keras.backend.tensorflow_backend as backend from threading import Thread
After that, we're going to go to the bottom of our script and:
if __name__ == '__main__':
FPS = 60
# For stats
ep_rewards = [-200]
# For more repetitive results
random.seed(1)
np.random.seed(1)
tf.set_random_seed(1)
# Memory fraction, used mostly when trai8ning multiple agents
gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=MEMORY_FRACTION)
backend.set_session(tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options)))
# Create models folder
if not os.path.isdir('models'):
os.makedirs('models')
# Create agent and environment
agent = DQNAgent()
env = CarEnv()
First, we set some FPS value (frames per second). When we start, we'll have high epsilon, which means a high probability that we'll be choosing an action randomly, rather than predicting it with our neural network. A random choice is going to be much faster than a predict operation, so we can arbitrarily delay this by setting some sort of general FPS. You should set this to be whatever your actual FPS is when epsilon is 0. We'll set random seeds for repeatable results, then specify GPU memory fraction. You might not need to do this, but seem to have issues with my RTX Titan, at least on Windows, running out of memory when it tries to allocate as much as possible.
Next we're making the models directory if it doesn't exist yet, this is where our models will go. Then we create our agent and environment class.
# Start training thread and wait for training to be initialized
trainer_thread = Thread(target=agent.train_in_loop, daemon=True)
trainer_thread.start()
while not agent.training_initialized:
time.sleep(0.01)
Start training thread and wait for training to be initialized, as the comment says!
# Initialize predictions - forst prediction takes longer as of initialization that has to be done
# It's better to do a first prediction then before we start iterating over episode steps
agent.get_qs(np.ones((env.im_height, env.im_width, 3)))
And now, we're ready to start iterating over however many episodes we set to do:
# Iterate over episodes
for episode in tqdm(range(1, EPISODES + 1), ascii=True, unit='episodes'):
#try:
env.collision_hist = []
# Update tensorboard step every episode
agent.tensorboard.step = episode
# Restarting episode - reset episode reward and step number
episode_reward = 0
step = 1
# Reset environment and get initial state
current_state = env.reset()
# Reset flag and start iterating until episode ends
done = False
episode_start = time.time()
Some initial values for our environments, and now we're ready to run. Basically an environment will run until it's done, so we can use a While True loop and break on our done flag.
As we play, we either want to take a random action, or figure out our current action based on our agent model:
# Play for given number of seconds only
while True:
# This part stays mostly the same, the change is to query a model for Q values
if np.random.random() > epsilon:
# Get action from Q table
action = np.argmax(agent.get_qs(current_state))
else:
# Get random action
action = np.random.randint(0, 3)
# This takes no time, so we add a delay matching 60 FPS (prediction above takes longer)
time.sleep(1/FPS)
Now, we will get our information from our environment's .step() method, which takes our action as a paramater:
new_state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
# Transform new continous state to new discrete state and count reward
episode_reward += reward
# Every step we update replay memory
agent.update_replay_memory((current_state, action, reward, new_state, done))
current_state = new_state
step += 1
if done:
break
Once we are done, what do we need to do? For one, we need to get rid of our actors:
# End of episode - destroy agents
for actor in env.actor_list:
actor.destroy()
Now for some stats + saving models that have a good reward (or any other rule you decide to set as an if statement:
# Append episode reward to a list and log stats (every given number of episodes)
ep_rewards.append(episode_reward)
if not episode % AGGREGATE_STATS_EVERY or episode == 1:
average_reward = sum(ep_rewards[-AGGREGATE_STATS_EVERY:])/len(ep_rewards[-AGGREGATE_STATS_EVERY:])
min_reward = min(ep_rewards[-AGGREGATE_STATS_EVERY:])
max_reward = max(ep_rewards[-AGGREGATE_STATS_EVERY:])
agent.tensorboard.update_stats(reward_avg=average_reward, reward_min=min_reward, reward_max=max_reward, epsilon=epsilon)
# Save model, but only when min reward is greater or equal a set value
if min_reward >= MIN_REWARD:
agent.model.save(f'models/{MODEL_NAME}__{max_reward:_>7.2f}max_{average_reward:_>7.2f}avg_{min_reward:_>7.2f}min__{int(time.time())}.model')
Next, let's decay epsilon:
# Decay epsilon
if epsilon > MIN_EPSILON:
epsilon *= EPSILON_DECAY
epsilon = max(MIN_EPSILON, epsilon)
Finally, if we've actually iterated through all of our target episodes, we can exit:
# Set termination flag for training thread and wait for it to finish
agent.terminate = True
trainer_thread.join()
agent.model.save(f'models/{MODEL_NAME}__{max_reward:_>7.2f}max_{average_reward:_>7.2f}avg_{min_reward:_>7.2f}min__{int(time.time())}.model')
And we're done, maybe.
Full code up to this point:
import glob
import os
import sys
import random
import time
import numpy as np
import cv2
import math
from collections import deque
from keras.applications.xception import Xception
from keras.layers import Dense, GlobalAveragePooling2D
from keras.optimizers import Adam
from keras.models import Model
from keras.callbacks import TensorBoard
import tensorflow as tf
import keras.backend.tensorflow_backend as backend
from threading import Thread
from tqdm import tqdm
try:
sys.path.append(glob.glob('../carla/dist/carla-*%d.%d-%s.egg' % (
sys.version_info.major,
sys.version_info.minor,
'win-amd64' if os.name == 'nt' else 'linux-x86_64'))[0])
except IndexError:
pass
import carla
SHOW_PREVIEW = False
IM_WIDTH = 640
IM_HEIGHT = 480
SECONDS_PER_EPISODE = 10
REPLAY_MEMORY_SIZE = 5_000
MIN_REPLAY_MEMORY_SIZE = 1_000
MINIBATCH_SIZE = 16
PREDICTION_BATCH_SIZE = 1
TRAINING_BATCH_SIZE = MINIBATCH_SIZE // 4
UPDATE_TARGET_EVERY = 5
MODEL_NAME = "Xception"
MEMORY_FRACTION = 0.4
MIN_REWARD = -200
EPISODES = 100
DISCOUNT = 0.99
epsilon = 1
EPSILON_DECAY = 0.95 ## 0.9975 99975
MIN_EPSILON = 0.001
AGGREGATE_STATS_EVERY = 10
# Own Tensorboard class
class ModifiedTensorBoard(TensorBoard):
# Overriding init to set initial step and writer (we want one log file for all .fit() calls)
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.step = 1
self.writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(self.log_dir)
# Overriding this method to stop creating default log writer
def set_model(self, model):
pass
# Overrided, saves logs with our step number
# (otherwise every .fit() will start writing from 0th step)
def on_epoch_end(self, epoch, logs=None):
self.update_stats(**logs)
# Overrided
# We train for one batch only, no need to save anything at epoch end
def on_batch_end(self, batch, logs=None):
pass
# Overrided, so won't close writer
def on_train_end(self, _):
pass
# Custom method for saving own metrics
# Creates writer, writes custom metrics and closes writer
def update_stats(self, **stats):
self._write_logs(stats, self.step)
class CarEnv:
SHOW_CAM = SHOW_PREVIEW
STEER_AMT = 1.0
im_width = IM_WIDTH
im_height = IM_HEIGHT
front_camera = None
def __init__(self):
self.client = carla.Client("localhost", 2000)
self.client.set_timeout(2.0)
self.world = self.client.get_world()
self.blueprint_library = self.world.get_blueprint_library()
self.model_3 = self.blueprint_library.filter("model3")[0]
def reset(self):
self.collision_hist = []
self.actor_list = []
self.transform = random.choice(self.world.get_map().get_spawn_points())
self.vehicle = self.world.spawn_actor(self.model_3, self.transform)
self.actor_list.append(self.vehicle)
self.rgb_cam = self.blueprint_library.find('sensor.camera.rgb')
self.rgb_cam.set_attribute("image_size_x", f"{self.im_width}")
self.rgb_cam.set_attribute("image_size_y", f"{self.im_height}")
self.rgb_cam.set_attribute("fov", f"110")
transform = carla.Transform(carla.Location(x=2.5, z=0.7))
self.sensor = self.world.spawn_actor(self.rgb_cam, transform, attach_to=self.vehicle)
self.actor_list.append(self.sensor)
self.sensor.listen(lambda data: self.process_img(data))
self.vehicle.apply_control(carla.VehicleControl(throttle=0.0, brake=0.0))
time.sleep(4)
colsensor = self.blueprint_library.find("sensor.other.collision")
self.colsensor = self.world.spawn_actor(colsensor, transform, attach_to=self.vehicle)
self.actor_list.append(self.colsensor)
self.colsensor.listen(lambda event: self.collision_data(event))
while self.front_camera is None:
time.sleep(0.01)
self.episode_start = time.time()
self.vehicle.apply_control(carla.VehicleControl(throttle=0.0, brake=0.0))
return self.front_camera
def collision_data(self, event):
self.collision_hist.append(event)
def process_img(self, image):
i = np.array(image.raw_data)
#print(i.shape)
i2 = i.reshape((self.im_height, self.im_width, 4))
i3 = i2[:, :, :3]
if self.SHOW_CAM:
cv2.imshow("", i3)
cv2.waitKey(1)
self.front_camera = i3
def step(self, action):
if action == 0:
self.vehicle.apply_control(carla.VehicleControl(throttle=1.0, steer=-1*self.STEER_AMT))
elif action == 1:
self.vehicle.apply_control(carla.VehicleControl(throttle=1.0, steer= 0))
elif action == 2:
self.vehicle.apply_control(carla.VehicleControl(throttle=1.0, steer=1*self.STEER_AMT))
v = self.vehicle.get_velocity()
kmh = int(3.6 * math.sqrt(v.x**2 + v.y**2 + v.z**2))
if len(self.collision_hist) != 0:
done = True
reward = -200
elif kmh < 50:
done = False
reward = -1
else:
done = False
reward = 1
if self.episode_start + SECONDS_PER_EPISODE < time.time():
done = True
return self.front_camera, reward, done, None
class DQNAgent:
def __init__(self):
self.model = self.create_model()
self.target_model = self.create_model()
self.target_model.set_weights(self.model.get_weights())
self.replay_memory = deque(maxlen=REPLAY_MEMORY_SIZE)
self.tensorboard = ModifiedTensorBoard(log_dir=f"logs/{MODEL_NAME}-{int(time.time())}")
self.target_update_counter = 0
self.graph = tf.get_default_graph()
self.terminate = False
self.last_logged_episode = 0
self.training_initialized = False
def create_model(self):
base_model = Xception(weights=None, include_top=False, input_shape=(IM_HEIGHT, IM_WIDTH,3))
x = base_model.output
x = GlobalAveragePooling2D()(x)
predictions = Dense(3, activation="linear")(x)
model = Model(inputs=base_model.input, outputs=predictions)
model.compile(loss="mse", optimizer=Adam(lr=0.001), metrics=["accuracy"])
return model
def update_replay_memory(self, transition):
# transition = (current_state, action, reward, new_state, done)
self.replay_memory.append(transition)
def train(self):
if len(self.replay_memory) < MIN_REPLAY_MEMORY_SIZE:
return
minibatch = random.sample(self.replay_memory, MINIBATCH_SIZE)
current_states = np.array([transition[0] for transition in minibatch])/255
with self.graph.as_default():
current_qs_list = self.model.predict(current_states, PREDICTION_BATCH_SIZE)
new_current_states = np.array([transition[3] for transition in minibatch])/255
with self.graph.as_default():
future_qs_list = self.target_model.predict(new_current_states, PREDICTION_BATCH_SIZE)
X = []
y = []
for index, (current_state, action, reward, new_state, done) in enumerate(minibatch):
if not done:
max_future_q = np.max(future_qs_list[index])
new_q = reward + DISCOUNT * max_future_q
else:
new_q = reward
current_qs = current_qs_list[index]
current_qs[action] = new_q
X.append(current_state)
y.append(current_qs)
log_this_step = False
if self.tensorboard.step > self.last_logged_episode:
log_this_step = True
self.last_log_episode = self.tensorboard.step
with self.graph.as_default():
self.model.fit(np.array(X)/255, np.array(y), batch_size=TRAINING_BATCH_SIZE, verbose=0, shuffle=False, callbacks=[self.tensorboard] if log_this_step else None)
if log_this_step:
self.target_update_counter += 1
if self.target_update_counter > UPDATE_TARGET_EVERY:
self.target_model.set_weights(self.model.get_weights())
self.target_update_counter = 0
def get_qs(self, state):
return self.model.predict(np.array(state).reshape(-1, *state.shape)/255)[0]
def train_in_loop(self):
X = np.random.uniform(size=(1, IM_HEIGHT, IM_WIDTH, 3)).astype(np.float32)
y = np.random.uniform(size=(1, 3)).astype(np.float32)
with self.graph.as_default():
self.model.fit(X,y, verbose=False, batch_size=1)
self.training_initialized = True
while True:
if self.terminate:
return
self.train()
time.sleep(0.01)
if __name__ == '__main__':
FPS = 60
# For stats
ep_rewards = [-200]
# For more repetitive results
random.seed(1)
np.random.seed(1)
tf.set_random_seed(1)
# Memory fraction, used mostly when trai8ning multiple agents
gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=MEMORY_FRACTION)
backend.set_session(tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options)))
# Create models folder
if not os.path.isdir('models'):
os.makedirs('models')
# Create agent and environment
agent = DQNAgent()
env = CarEnv()
# Start training thread and wait for training to be initialized
trainer_thread = Thread(target=agent.train_in_loop, daemon=True)
trainer_thread.start()
while not agent.training_initialized:
time.sleep(0.01)
# Initialize predictions - forst prediction takes longer as of initialization that has to be done
# It's better to do a first prediction then before we start iterating over episode steps
agent.get_qs(np.ones((env.im_height, env.im_width, 3)))
# Iterate over episodes
for episode in tqdm(range(1, EPISODES + 1), ascii=True, unit='episodes'):
#try:
env.collision_hist = []
# Update tensorboard step every episode
agent.tensorboard.step = episode
# Restarting episode - reset episode reward and step number
episode_reward = 0
step = 1
# Reset environment and get initial state
current_state = env.reset()
# Reset flag and start iterating until episode ends
done = False
episode_start = time.time()
# Play for given number of seconds only
while True:
# This part stays mostly the same, the change is to query a model for Q values
if np.random.random() > epsilon:
# Get action from Q table
action = np.argmax(agent.get_qs(current_state))
else:
# Get random action
action = np.random.randint(0, 3)
# This takes no time, so we add a delay matching 60 FPS (prediction above takes longer)
time.sleep(1/FPS)
new_state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
# Transform new continous state to new discrete state and count reward
episode_reward += reward
# Every step we update replay memory
agent.update_replay_memory((current_state, action, reward, new_state, done))
current_state = new_state
step += 1
if done:
break
# End of episode - destroy agents
for actor in env.actor_list:
actor.destroy()
# Append episode reward to a list and log stats (every given number of episodes)
ep_rewards.append(episode_reward)
if not episode % AGGREGATE_STATS_EVERY or episode == 1:
average_reward = sum(ep_rewards[-AGGREGATE_STATS_EVERY:])/len(ep_rewards[-AGGREGATE_STATS_EVERY:])
min_reward = min(ep_rewards[-AGGREGATE_STATS_EVERY:])
max_reward = max(ep_rewards[-AGGREGATE_STATS_EVERY:])
agent.tensorboard.update_stats(reward_avg=average_reward, reward_min=min_reward, reward_max=max_reward, epsilon=epsilon)
# Save model, but only when min reward is greater or equal a set value
if min_reward >= MIN_REWARD:
agent.model.save(f'models/{MODEL_NAME}__{max_reward:_>7.2f}max_{average_reward:_>7.2f}avg_{min_reward:_>7.2f}min__{int(time.time())}.model')
# Decay epsilon
if epsilon > MIN_EPSILON:
epsilon *= EPSILON_DECAY
epsilon = max(MIN_EPSILON, epsilon)
# Set termination flag for training thread and wait for it to finish
agent.terminate = True
trainer_thread.join()
agent.model.save(f'models/{MODEL_NAME}__{max_reward:_>7.2f}max_{average_reward:_>7.2f}avg_{min_reward:_>7.2f}min__{int(time.time())}.model')
Let's go ahead and run that, it will run 100 episodes. 100 episodes took 17 minutes on a Titan RTX.
You should have gotten some log files, let's check those out.
tensorboard --logdir=logs/
Depending on your OS, what you need to navigate to may vary. On linux, whatever it tells you (should give you a URL in the console output) should suffice, probably 127.0.0.1:6006 will work too. On windows, I find the only thing that works for me is localhost:6006. Whatever you gotta do to get there! Anyway, once there, we can just search for tags matching the following regex: \w (any letter) and see all of our graphs together. For me, I have:
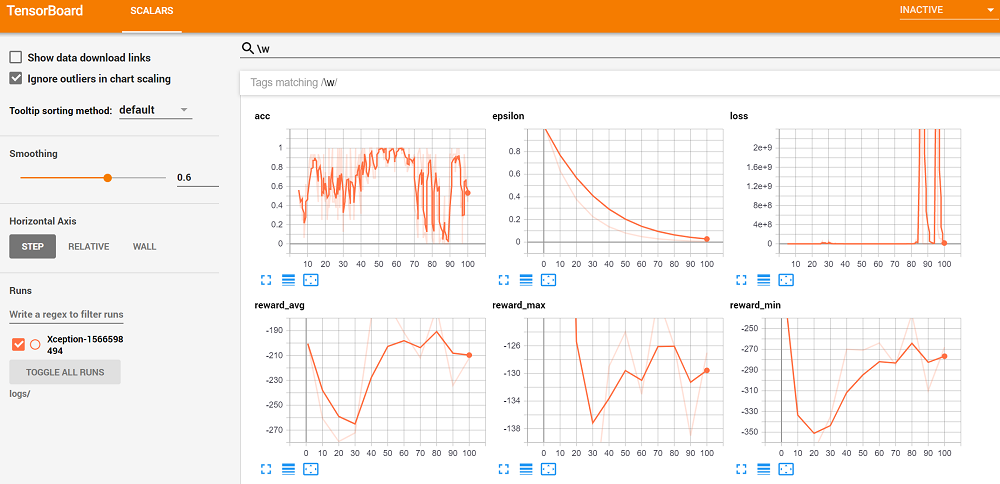
So, not too surprisingly, we didn't suddenly learn how to be incredible drivers in 100 episodes (judging by our average reward), so we probably should cancel those investor meetings for pitching the next billion-dollar self-driving car startup.
I forgot to add the model.save to my code the first time I tested, so I ended up running again. This time around, I actually got better-looking results. Notice mainly how loss was able to seemingly recover from the explosion.
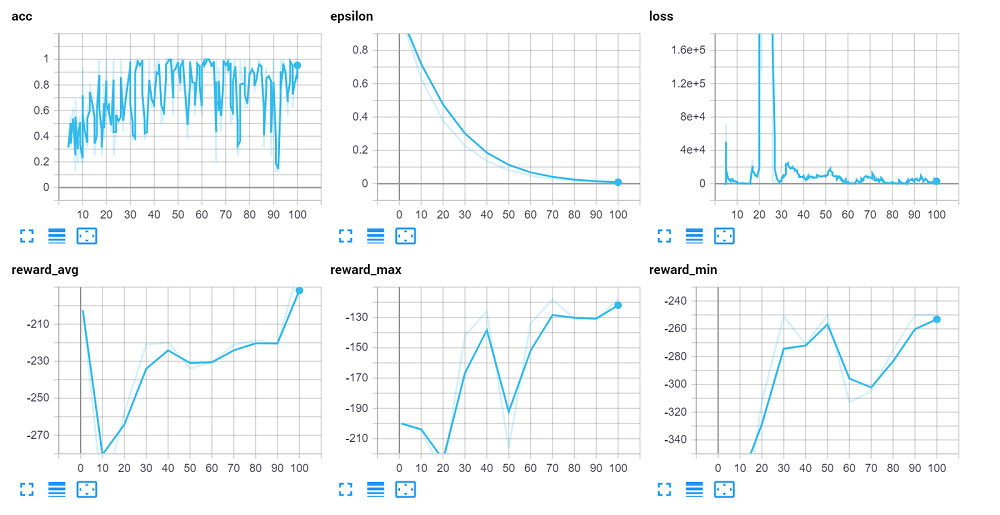
Now, we've only done 100 episodes. I suspect we'll need more like 100,000 episodes to see anything decent, provided the rest of our issues are solved as well. That said, it can be helpful to *see* your actual agent running. So here's a quick script to just play and see your models in action:
import random
from collections import deque
import numpy as np
import cv2
import time
import tensorflow as tf
import keras.backend.tensorflow_backend as backend
from keras.models import load_model
from tutorial5_code import CarEnv, MEMORY_FRACTION
MODEL_PATH = 'models/Xception__-118.00max_-179.10avg_-250.00min__1566603992.model'
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Memory fraction
gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=MEMORY_FRACTION)
backend.set_session(tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options)))
# Load the model
model = load_model(MODEL_PATH)
# Create environment
env = CarEnv()
# For agent speed measurements - keeps last 60 frametimes
fps_counter = deque(maxlen=60)
# Initialize predictions - first prediction takes longer as of initialization that has to be done
# It's better to do a first prediction then before we start iterating over episode steps
model.predict(np.ones((1, env.im_height, env.im_width, 3)))
# Loop over episodes
while True:
print('Restarting episode')
# Reset environment and get initial state
current_state = env.reset()
env.collision_hist = []
done = False
# Loop over steps
while True:
# For FPS counter
step_start = time.time()
# Show current frame
cv2.imshow(f'Agent - preview', current_state)
cv2.waitKey(1)
# Predict an action based on current observation space
qs = model.predict(np.array(current_state).reshape(-1, *current_state.shape)/255)[0]
action = np.argmax(qs)
# Step environment (additional flag informs environment to not break an episode by time limit)
new_state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
# Set current step for next loop iteration
current_state = new_state
# If done - agent crashed, break an episode
if done:
break
# Measure step time, append to a deque, then print mean FPS for last 60 frames, q values and taken action
frame_time = time.time() - step_start
fps_counter.append(frame_time)
print(f'Agent: {len(fps_counter)/sum(fps_counter):>4.1f} FPS | Action: [{qs[0]:>5.2f}, {qs[1]:>5.2f}, {qs[2]:>5.2f}] {action}')
# Destroy an actor at end of episode
for actor in env.actor_list:
actor.destroy()
Rename the import tutorial5_code to whatever you called your RL agent/env/trainer script, and then fix the MODEL_PATH = 'models/Xception__-118.00max_-179.10avg_-250.00min__1566603992.model' that you use, since your model name will be different from mine.
For example, here's my agent in action:
Again, I need to stress, this is ONLY 100 EPISODES. But, we can see agent has learned to really just do 1 thing. Agent might learn to just do one thing because your Q values are actually static (model outputs same Q values no matter the input), or, like in our case, they are all actually changing, it's just turn right is always consistently higher.
Another thing I see here is sometimes turn left is higher than turn straight, other times turn straight is higher than left. So there's still some hope/promise. One thing I learned in the Self-driving cars in GTA V series is that you can just get away with adding an output layer weight.
For example, in the play script, you could modify qs by doing:
qs = model.predict(np.array(current_state).reshape(-1, *current_state.shape)/255)[0]
qs *= [0.975, 1, 0.92]
action = np.argmax(qs)
So this acts as one final layer to your network. Again, this really isn't gonna help us with a 100-episode model. The next thing we've found is it's likely better to go ahead and just keep rewards as -1 and positive 1. No more -200. We found that this was likely exploding the Q values, which later seemingly exploded the loss and just caused mayhem. We may even do further clipping.
The next change we've made is actually simplifying our neural network to something like a 2-3 layer CNN with something like 64-256 features each. Not sure yet, but simpler seems better, less parameters to learn. For fully-supervised learning, I think more parameters worked well because everything was a "ground truth." For reinforcement learning, I think it's just too hard for the AI to dig itself out of the hole of stupidity that it's starting with by trying to train 10s of millions of weights.
Anyway, that's all for this tutorial. In the next tutorial, I will bring you a working model and tell you how I did it.
-
Introduction - Self-driving cars with Carla and Python part 1
-
Controlling the Car and getting sensor data - Self-driving cars with Carla and Python part 2
-
Reinforcement Learning Environment - Self-driving cars with Carla and Python part 3
-
Reinforcement Learning Agent - Self-driving cars with Carla and Python part 4
-
Reinforcement Learning in Action - Self-driving cars with Carla and Python part 5
-
Longer-term model results - Self-driving cars with Carla and Python