Tokenizing Words and Sentences with NLTK
Welcome to a Natural Language Processing tutorial series, using the Natural Language Toolkit, or NLTK, module with Python.
The NLTK module is a massive tool kit, aimed at helping you with the entire Natural Language Processing (NLP) methodology. NLTK will aid you with everything from splitting sentences from paragraphs, splitting up words, recognizing the part of speech of those words, highlighting the main subjects, and then even with helping your machine to understand what the text is all about. In this series, we're going to tackle the field of opinion mining, or sentiment analysis.
In our path to learning how to do sentiment analysis with NLTK, we're going to learn the following:
- Tokenizing - Splitting sentences and words from the body of text.
- Part of Speech tagging
- Machine Learning with the Naive Bayes classifier
- How to tie in Scikit-learn (sklearn) with NLTK
- Training classifiers with datasets
- Performing live, streaming, sentiment analysis with Twitter.
- ...and much more.
In order to get started, you are going to need the NLTK module, as well as Python.
If you do not have Python yet, go to Python.org and download the latest version of Python if you are on Windows. If you are on Mac or Linux, you should be able to run an apt-get install python3
Next, you're going to need NLTK 3. The easiest method to installing the NLTK module is going to be with pip.
For all users, that is done by opening up cmd.exe, bash, or whatever shell you use and typing:pip install nltk
Next, we need to install some of the components for NLTK. Open python via whatever means you normally do, and type:
import nltk nltk.download()
Unless you are operating headless, a GUI will pop up like this, only probably with red instead of green:
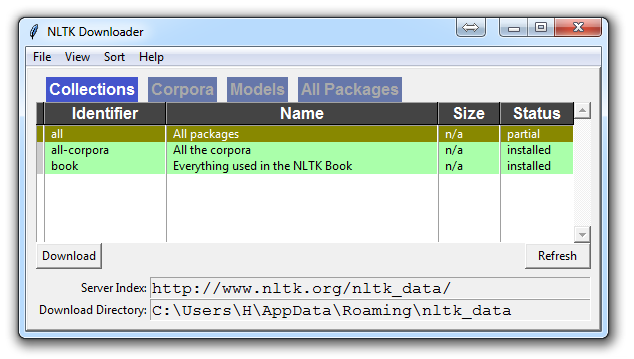
Choose to download "all" for all packages, and then click 'download.' This will give you all of the tokenizers, chunkers, other algorithms, and all of the corpora. If space is an issue, you can elect to selectively download everything manually. The NLTK module will take up about 7MB, and the entire nltk_data directory will take up about 1.8GB, which includes your chunkers, parsers, and the corpora.
If you are operating headless, like on a VPS, you can install everything by running Python and doing:
import nltk
nltk.download()
d (for download)
all (for download everything)
That will download everything for you headlessly.
Now that you have all the things that you need, let's knock out some quick vocabulary:
- Corpus - Body of text, singular. Corpora is the plural of this. Example: A collection of medical journals.
- Lexicon - Words and their meanings. Example: English dictionary. Consider, however, that various fields will have different lexicons. For example: To a financial investor, the first meaning for the word "Bull" is someone who is confident about the market, as compared to the common English lexicon, where the first meaning for the word "Bull" is an animal. As such, there is a special lexicon for financial investors, doctors, children, mechanics, and so on.
- Token - Each "entity" that is a part of whatever was split up based on rules. For examples, each word is a token when a sentence is "tokenized" into words. Each sentence can also be a token, if you tokenized the sentences out of a paragraph.
These are the words you will most commonly hear upon entering the Natural Language Processing (NLP) space, but there are many more that we will be covering in time. With that, let's show an example of how one might actually tokenize something into tokens with the NLTK module.
from nltk.tokenize import sent_tokenize, word_tokenize EXAMPLE_TEXT = "Hello Mr. Smith, how are you doing today? The weather is great, and Python is awesome. The sky is pinkish-blue. You shouldn't eat cardboard." print(sent_tokenize(EXAMPLE_TEXT))
At first, you may think tokenizing by things like words or sentences is a rather trivial enterprise. For many sentences it can be. The first step would be likely doing a simple .split('. '), or splitting by period followed by a space. Then maybe you would bring in some regular expressions to split by period, space, and then a capital letter. The problem is that things like Mr. Smith would cause you trouble, and many other things. Splitting by word is also a challenge, especially when considering things like concatenations like we and are to we're. NLTK is going to go ahead and just save you a ton of time with this seemingly simple, yet very complex, operation.
The above code will output the sentences, split up into a list of sentences, which you can do things like iterate through with a for loop.['Hello Mr. Smith, how are you doing today?', 'The weather is great, and Python is awesome.', 'The sky is pinkish-blue.', "You shouldn't eat cardboard."]
So there, we have created tokens, which are sentences. Let's tokenize by word instead this time:
print(word_tokenize(EXAMPLE_TEXT))
Now our output is: ['Hello', 'Mr.', 'Smith', ',', 'how', 'are', 'you', 'doing', 'today', '?', 'The', 'weather', 'is', 'great', ',', 'and', 'Python', 'is', 'awesome', '.', 'The', 'sky', 'is', 'pinkish-blue', '.', 'You', 'should', "n't", 'eat', 'cardboard', '.']
There are a few things to note here. First, notice that punctuation is treated as a separate token. Also, notice the separation of the word "shouldn't" into "should" and "n't." Finally, notice that "pinkish-blue" is indeed treated like the "one word" it was meant to be turned into. Pretty cool!
Now, looking at these tokenized words, we have to begin thinking about what our next step might be. We start to ponder about how might we derive meaning by looking at these words. We can clearly think of ways to put value to many words, but we also see a few words that are basically worthless. These are a form of "stop words," which we can also handle for. That is what we're going to be talking about in the next tutorial.
There exists 4 quiz/question(s) for this tutorial. for access to these, video downloads, and no ads.
-
Tokenizing Words and Sentences with NLTK
-
Stop words with NLTK
-
Stemming words with NLTK
-
Part of Speech Tagging with NLTK
-
Chunking with NLTK
-
Chinking with NLTK
-
Named Entity Recognition with NLTK
-
Lemmatizing with NLTK
-
The corpora with NLTK
-
Wordnet with NLTK
-
Text Classification with NLTK
-
Converting words to Features with NLTK
-
Naive Bayes Classifier with NLTK
-
Saving Classifiers with NLTK
-
Scikit-Learn Sklearn with NLTK
-
Combining Algorithms with NLTK
-
Investigating bias with NLTK
-
Improving Training Data for sentiment analysis with NLTK
-
Creating a module for Sentiment Analysis with NLTK
-
Twitter Sentiment Analysis with NLTK
-
Graphing Live Twitter Sentiment Analysis with NLTK with NLTK
-
Named Entity Recognition with Stanford NER Tagger
-
Testing NLTK and Stanford NER Taggers for Accuracy
-
Testing NLTK and Stanford NER Taggers for Speed
-
Using BIO Tags to Create Readable Named Entity Lists